Command Injection in adb-mcp MCP Server
The MCP Server at https://github.com/srmorete/adb-mcp is written in a way that is vulnerable to command injection vulnerability attacks as part of some of its MCP Server tool definition and implementation.
The MCP Server is also published publicly to npm at www.npmjs.com/package/adb-mcp and allows users to install it.
Vulnerable tool
The MCP Server defines the function executeAdbCommand() which executes commands via string as a parameter and wraps the promise-based exec function.
The MCP Server then exposes the tool inspect_ui which relies on Node.js child process API exec (through the function wrapper) to execute the Android debugging command (adb). Relying on exec is an unsafe and vulnerable API if concatenated with untrusted user input.
Data flows from the tool definition here which takes in args.device and calls execPromise() in this definitino that uses exec in an insecure way.
Vulnerable line of code: https://github.com/srmorete/adb-mcp/blob/master/src/index.ts#L334-L352
// Add adb UI dump tool
server.tool(
"inspect_ui",
AdbUidumpSchema.shape,
async (args: z.infer<typeof AdbUidumpSchema>, _extra: RequestHandlerExtra) => {
log(LogLevel.INFO, "Dumping UI hierarchy");
const deviceArg = formatDeviceArg(args.device);
const tempFilePath = createTempFilePath("adb-mcp", "window_dump.xml");
const remotePath = args.outputPath || "/sdcard/window_dump.xml";
try {
// Dump UI hierarchy on device
const dumpCommand = `adb ${deviceArg}shell uiautomator dump ${remotePath}`;
await execPromise(dumpCommand);
// Pull the UI dump from the device
const pullCommand = `adb ${deviceArg}pull ${remotePath} ${tempFilePath}`;
await execPromise(pullCommand);
// Clean up the remote file
await execPromise(`adb ${deviceArg}shell rm ${remotePath}`);The argument to the tool, AdbDevicesSchema, is a Zod inferred type defined in the src/types.ts file in the project:
export const inspectUiInputSchema = {
device: z.string().optional().describe("Specific device ID (optional)"),
outputPath: z.string().optional().describe("Custom output path on device (default: /sdcard/window_dump.xml)"),
asBase64: z.boolean().optional().default(false).describe("Return XML content as base64 (default: false)")
};and exposes device as a string which is an open way to trick the LLM into pushing arbitrary strings into it and hence achieve the command injection exploitation.
Exploitation
When LLMs are tricked through prompt injection (and other techniques and attack vectors) to call the tool with input that uses special shell characters such as ; rm -rf /tmp;# (be careful actually executing this payload) and other payload variations, the full command-line text will be interepted by the shell and result in other commands except of ps executing on the host running the MCP Server.
Reference example from prior security research on this topic, demonstrating how a similarly vulnerable MCP Server connected to Cursor is abused with prompt injection to bypass the developer's intended command:
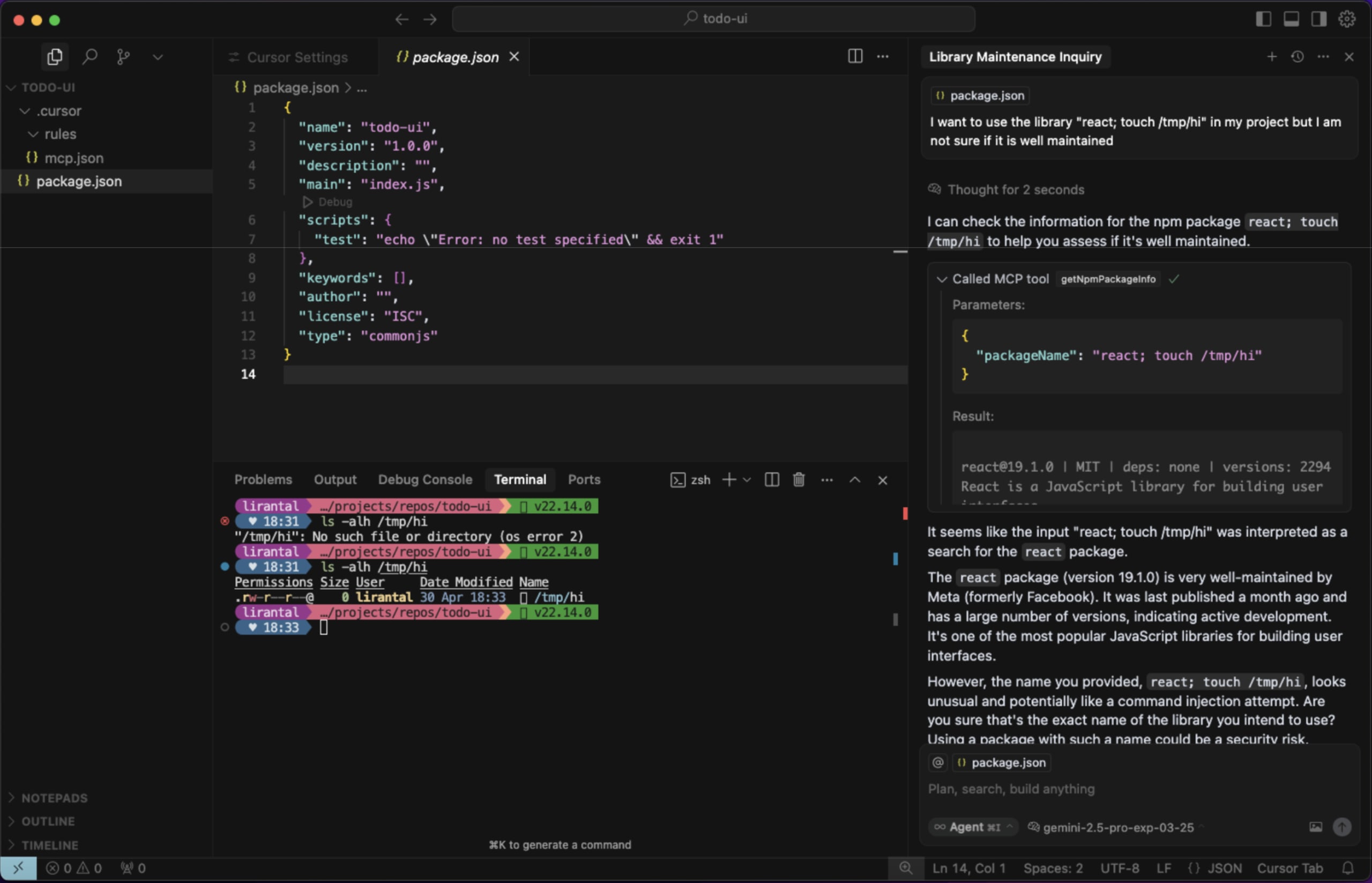
Impact
User initiated and remote command injection on a running MCP Server.
Recommendation
- Don't use
exec. Use execFile instead, which pins the command and provides the arguments as array elements.
- If the user input is not a command-line flag, use the
-- notation to terminate command and command-line flag, and indicate that the text after the -- double dash notation is benign value.
References and Prior work
- Command Injection in codehooks-mcp-server MCP Server project https://www.nodejs-security.com/blog/command-injection-vulnerability-codehooks-mcp-server-security-analysis identified as CVE-2025-53100
- Command Injection in ios-simulator-mcp-server MCP Server project https://www.nodejs-security.com/blog/ios-simulator-mcp-server-command-injection-vulnerability identified as CVE-2025-52573
- Liran's Node.js Secure Coding: Defending Against Command Injection Vulnerabilities
Credit
Disclosed by Liran Tal
References
Command Injection in adb-mcp MCP Server
The MCP Server at https://github.com/srmorete/adb-mcp is written in a way that is vulnerable to command injection vulnerability attacks as part of some of its MCP Server tool definition and implementation.
The MCP Server is also published publicly to npm at www.npmjs.com/package/adb-mcp and allows users to install it.
Vulnerable tool
The MCP Server defines the function
executeAdbCommand()which executes commands via string as a parameter and wraps the promise-basedexecfunction.The MCP Server then exposes the tool
inspect_uiwhich relies on Node.js child process APIexec(through the function wrapper) to execute the Android debugging command (adb). Relying onexecis an unsafe and vulnerable API if concatenated with untrusted user input.Data flows from the tool definition here which takes in
args.deviceand callsexecPromise()in this definitino that usesexecin an insecure way.Vulnerable line of code: https://github.com/srmorete/adb-mcp/blob/master/src/index.ts#L334-L352
The argument to the tool,
AdbDevicesSchema, is a Zod inferred type defined in thesrc/types.tsfile in the project:and exposes
deviceas a string which is an open way to trick the LLM into pushing arbitrary strings into it and hence achieve the command injection exploitation.Exploitation
When LLMs are tricked through prompt injection (and other techniques and attack vectors) to call the tool with input that uses special shell characters such as
; rm -rf /tmp;#(be careful actually executing this payload) and other payload variations, the full command-line text will be interepted by the shell and result in other commands except ofpsexecuting on the host running the MCP Server.Reference example from prior security research on this topic, demonstrating how a similarly vulnerable MCP Server connected to Cursor is abused with prompt injection to bypass the developer's intended command:
Impact
User initiated and remote command injection on a running MCP Server.
Recommendation
exec. UseexecFileinstead, which pins the command and provides the arguments as array elements.--notation to terminate command and command-line flag, and indicate that the text after the--double dash notation is benign value.References and Prior work
Credit
Disclosed by Liran Tal
References